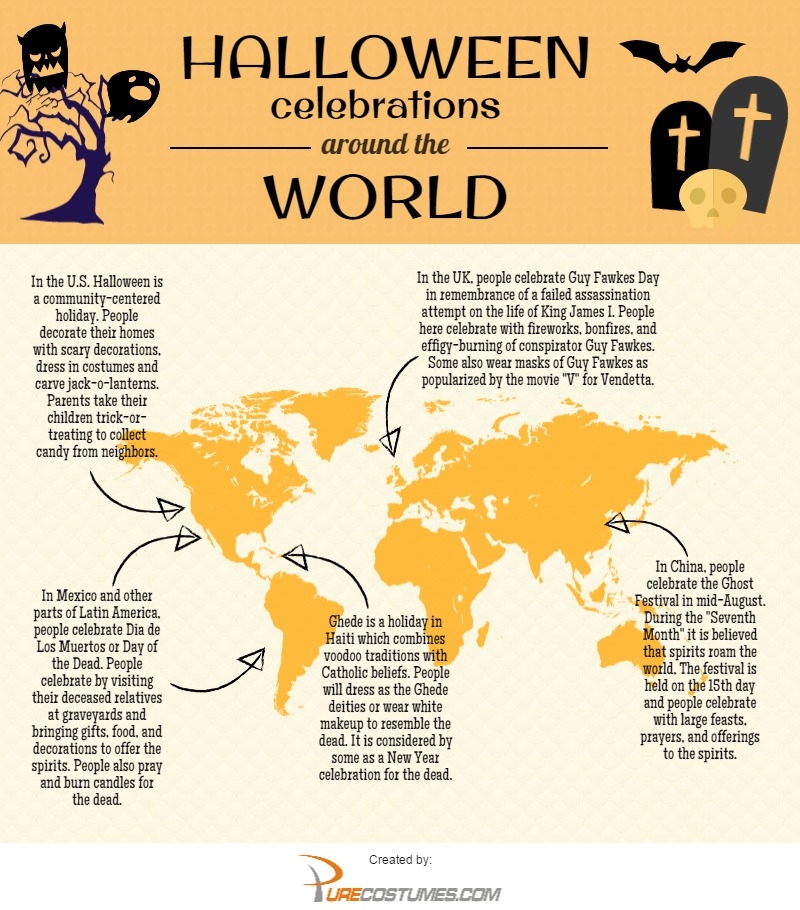
Halloween, the annual celebration on October 31st, is often associated with trick-or-treating, spooky costumes, and jack-o’-lanterns. However, this holiday’s origins and practices extend far beyond the Western world, revealing a fascinating tapestry of cultural influences and interpretations. While Halloween’s modern form is largely rooted in Western traditions, exploring its global variations unveils a rich history of ancient customs, spiritual beliefs, and seasonal festivals.
The Roots of Halloween: From Ancient Celtic Origins to Christian Influence
Halloween’s roots can be traced back to the ancient Celtic festival of Samhain, celebrated on October 31st. The Celts, who inhabited parts of Ireland, Britain, and northern France, believed that on this night, the veil between the worlds of the living and the dead thinned, allowing spirits to cross over. This occasion was marked by bonfires, feasts, and divination rituals.
The arrival of Christianity in Europe led to a gradual assimilation of Samhain into the Christian calendar. In the 8th century, Pope Gregory IV designated November 1st as All Saints’ Day, a day to honor Christian saints. The day following, November 2nd, became All Souls’ Day, dedicated to remembering the dead. Over time, these Christian observances intertwined with the Celtic traditions of Samhain, resulting in the modern Halloween we know today.
Beyond the West: Exploring Halloween’s Global Variations
While Halloween’s Western origins are well-documented, it’s important to recognize that similar celebrations of death, ancestors, and the transition between seasons exist across the globe. These celebrations, often predating Halloween’s Christianization, offer unique insights into the diverse ways cultures engage with the concept of the afterlife and the changing seasons.
1. Mexico: Día de los Muertos (Day of the Dead)
Día de los Muertos, a vibrant and joyous celebration observed in Mexico and other Latin American countries, is a prime example of how Halloween traditions have evolved independently. Held on November 1st and 2nd, this holiday honors the deceased with offerings of food, drinks, flowers, and personal mementos. The celebration is characterized by colorful altars, sugar skulls, and vibrant decorations, creating a festive atmosphere that celebrates life and death in a harmonious balance.
2. China: Ghost Festival
The Chinese Ghost Festival, known as Zhongyuan Jie, is a significant religious holiday observed on the 15th day of the seventh lunar month. This festival, deeply rooted in Taoist and Buddhist beliefs, is dedicated to honoring ancestors and appeasing wandering spirits. The celebration involves offerings of food and incense, paper money burning, and various rituals aimed at ensuring the well-being of deceased loved ones.
3. Japan: Obon
Obon, a Buddhist custom observed in Japan, is a period for remembering ancestors and welcoming their spirits back to the living world. Typically held in mid-August, Obon involves visiting family graves, lighting lanterns to guide ancestral spirits, and offering food and incense as tokens of respect. The celebration is also marked by traditional Bon Odori dances, which serve as a way to entertain the spirits and foster a sense of communal joy.
4. India: Diwali
Diwali, the Festival of Lights, celebrated by Hindus, Sikhs, and Jains in India and other parts of the world, is a five-day festival that marks the triumph of good over evil. While not directly related to Halloween, Diwali shares similarities in its focus on light, symbolic purification, and the celebration of life. The festival is characterized by the lighting of diyas (clay lamps), fireworks, and the exchange of sweets and gifts.
5. Africa: Ancestral Celebrations
Across various African cultures, celebrations honoring ancestors and the spirits of the departed are prevalent. These celebrations often involve offerings of food, libations, and rituals aimed at maintaining a harmonious relationship with the spirit world. These traditions underscore the importance of honoring the legacy of ancestors and seeking their guidance and protection.
Understanding the Significance of Global Halloween Variations
Exploring Halloween’s global variations offers a unique opportunity to gain a deeper understanding of cultural diversity and the ways in which different societies engage with the concepts of death, the afterlife, and the cycle of life. These celebrations provide valuable insights into the shared human experience of loss, remembrance, and the enduring connection between the living and the dead.
Benefits of Exploring Halloween’s Global Variations
-
Promoting Cultural Understanding: By learning about how other cultures celebrate Halloween, we can gain a broader perspective on the world and foster a greater appreciation for different traditions and beliefs.
-
Enhancing Global Citizenship: Understanding diverse perspectives on Halloween contributes to our understanding of global interconnectedness and promotes empathy and tolerance for different cultures.
-
Inspiring Creativity and Innovation: The exploration of global Halloween traditions can spark creativity and inspire new ways of celebrating the holiday, incorporating elements from different cultures.
-
Preserving Cultural Heritage: By recognizing and appreciating the diversity of Halloween celebrations, we contribute to the preservation of cultural heritage and ensure the continuity of these traditions for future generations.
FAQs: Exploring Halloween’s Global Variations
1. What is the origin of Halloween?
Halloween’s origins can be traced back to the ancient Celtic festival of Samhain, celebrated on October 31st. The Celts believed that on this night, the veil between the worlds of the living and the dead thinned, allowing spirits to cross over.
2. How did Halloween evolve into its modern form?
The arrival of Christianity in Europe led to the assimilation of Samhain into the Christian calendar. All Saints’ Day and All Souls’ Day, celebrated on November 1st and 2nd, respectively, gradually intertwined with Celtic traditions, shaping the modern Halloween we know today.
3. What are some examples of Halloween celebrations in other cultures?
Examples include Día de los Muertos in Mexico, the Chinese Ghost Festival, Obon in Japan, Diwali in India, and various ancestral celebrations in Africa.
4. What are the key differences between Halloween and other global celebrations?
While Halloween often focuses on costumes, trick-or-treating, and spooky themes, other celebrations, such as Día de los Muertos, emphasize honoring ancestors and celebrating life and death in a more joyful and celebratory manner.
5. What is the significance of exploring Halloween’s global variations?
Exploring global variations of Halloween promotes cultural understanding, enhances global citizenship, inspires creativity, and contributes to the preservation of cultural heritage.
Tips for Exploring Halloween’s Global Variations
-
Research online: Explore online resources, articles, and documentaries that delve into the history and practices of Halloween celebrations in different cultures.
-
Visit museums and cultural centers: Museums and cultural centers often host exhibitions and events that showcase the diversity of Halloween traditions worldwide.
-
Attend cultural festivals: Participate in cultural festivals and events that celebrate Halloween or similar holidays in other cultures.
-
Engage with communities: Connect with individuals from different cultural backgrounds to learn about their perspectives on Halloween and related traditions.
-
Share your knowledge: Share your insights and learnings with others to promote understanding and appreciation for global Halloween variations.
Conclusion: Embracing the Diversity of Halloween Celebrations
Exploring Halloween in different cultures reveals a fascinating tapestry of human experiences, beliefs, and traditions. By recognizing and celebrating the diversity of these celebrations, we gain a deeper appreciation for the rich cultural heritage of our world and foster a greater sense of understanding and interconnectedness. As we celebrate Halloween, let us remember that this holiday’s origins and practices extend far beyond the Western world, offering a valuable opportunity to learn from and connect with diverse cultures across the globe.